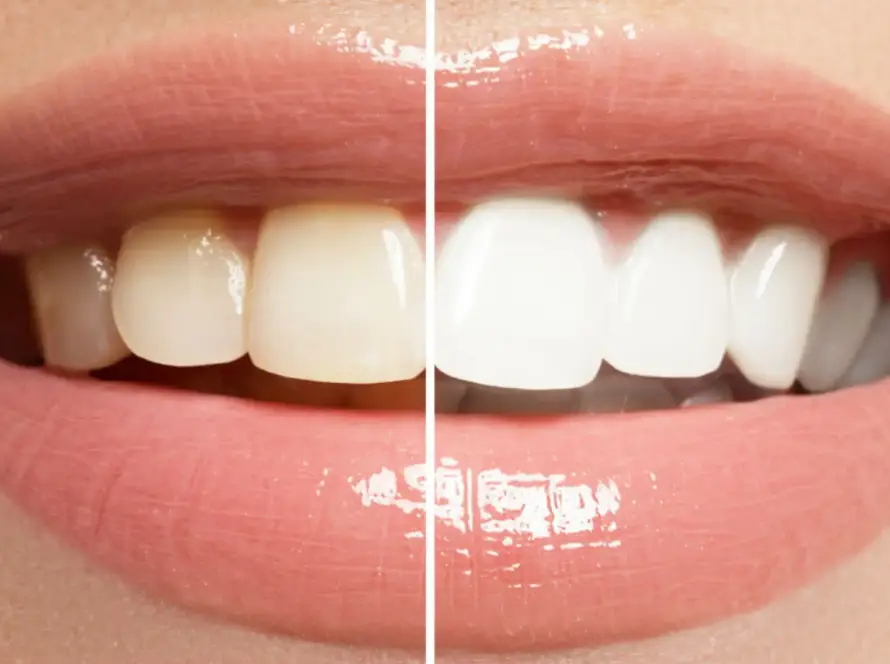
Sensitive teeth can often be a source of discomfort or pain for individuals. It is characterized by a sharp, sudden, or lingering pain in the teeth when exposed to certain stimuli such as hot or cold temperatures, sweet or acidic foods and drinks, or even while brushing or flossing. This condition occurs when the tooth enamel, which is the protective outer layer of the tooth, becomes worn down or the gum line recedes, exposing the underlying dentin. Dentin contains tiny tubules that allow stimuli to reach the nerves of the tooth, causing sensitivity.
There can be several factors that contribute to the development of sensitive teeth. These can include:
- Brushing too aggressively: Frequent and harsh brushing can lead to the erosion of tooth enamel, causing tooth sensitivity.
- Tooth decay: Cavities and tooth decay can cause sensitivity as the bacteria reach the nerves inside the tooth.
- Gum disease: When the gums recede, the roots of the teeth become exposed, leading to sensitivity.
- Teeth grinding: Continuous grinding of teeth can wear down the enamel and expose the dentin, resulting in sensitivity.
- Dental procedures: Certain dental procedures, such as teeth whitening or the placement of dental crowns, can cause temporary sensitivity.
Understanding the causes of tooth sensitivity is crucial in determining the appropriate treatment options. By addressing the underlying issue, individuals can find relief from the discomfort and protect their teeth from further damage.
Common Causes of Tooth Sensitivity
There are several common causes of tooth sensitivity that can lead to discomfort and pain. These include:
- Tooth enamel erosion: When the protective outer layer of the tooth called enamel wears away, it exposes the underlying dentin, which is more sensitive to hot, cold, and acidic foods and beverages.
- Gum recession: Receding gums can expose the tooth roots, which are not covered by enamel and are more sensitive to temperature changes.
- Tooth decay: Cavities or tooth decay can cause sensitivity when the enamel becomes damaged, exposing the sensitive dentin.
- Fractured teeth: Cracked or chipped teeth can expose the inner layers of the tooth, leading to tooth sensitivity.
- Aggressive brushing: Brushing your teeth too hard or using a toothbrush with hard bristles can wear away the enamel and cause tooth sensitivity.
- Teeth grinding: The habit of grinding or clenching your teeth can wear down the enamel, making the teeth more sensitive.
- Acidic foods and beverages: Consuming acidic foods and drinks, such as citrus fruits, soda, or wine, can erode the tooth enamel and lead to sensitivity.
- Dental procedures: Some dental procedures, such as teeth whitening treatments or the placement of dental crowns, can temporarily cause tooth sensitivity.
Understanding the common causes of tooth sensitivity can help individuals take preventive measures and seek appropriate treatment to alleviate discomfort and maintain oral health.
Dental Conditions Associated with Tooth Sensitivity
There are several dental conditions that can contribute to tooth sensitivity. Understanding these conditions can help in identifying the underlying cause and seeking appropriate treatment. Some common dental conditions associated with tooth sensitivity include:
- Tooth Decay: When the protective layer of enamel on the tooth surface wears away due to poor oral hygiene or acidic food and drinks, it can lead to tooth decay. As the decay progresses, it exposes the sensitive inner layers of the tooth, causing sensitivity to hot, cold, sweet, or acidic foods and beverages.
- Gum Disease: Periodontal disease, also known as gum disease, can lead to receding gums. When the gums recede, the roots of the teeth become exposed, making them sensitive to temperature and touch.
- Dental Erosion: Erosion occurs when the tooth enamel is worn away by acid, often from consuming too many acidic food and drinks or from acid reflux. Tooth sensitivity may occur as the layers beneath the enamel become exposed.
- Fractured Teeth: Teeth that are cracked or chipped can expose the sensitive dentin layer beneath the enamel. This can result in tooth sensitivity, especially when biting or chewing.
- Bruxism: Grinding or clenching of teeth, known as bruxism, can lead to tooth sensitivity. The constant pressure and friction can wear down the enamel, exposing the sensitive dentin layer.
- Dental Procedures: Certain dental treatments such as teeth whitening, fillings, or crown placements can cause temporary tooth sensitivity. This sensitivity usually subsides after a short period, but it is essential to discuss any prolonged sensitivity with a dentist.
It is crucial to consult a dentist if you experience tooth sensitivity. They can perform a thorough examination and determine the underlying cause of your sensitivity to provide appropriate treatment options and alleviate discomfort.
Lifestyle Factors that Contribute to Tooth Sensitivity
- Poor oral hygiene: Neglecting proper oral hygiene practices, such as inadequate brushing or flossing, can lead to the buildup of plaque and tartar. This accumulation can cause the erosion of tooth enamel, exposing the sensitive dentin underneath.
- Consuming acidic foods and drinks: Regularly consuming acidic foods and drinks, such as citrus fruits, soda, and sports drinks, can gradually wear down tooth enamel. As the enamel becomes thinner, the nerve endings within the teeth may become more exposed, leading to tooth sensitivity.
- Aggressive brushing: Brushing your teeth too vigorously or using a toothbrush with hard bristles can cause enamel erosion and gum recession. This can expose the sensitive dentin and lead to tooth sensitivity.
- Teeth grinding or clenching: Habitual teeth grinding or clenching, often during sleep, can wear down the enamel and expose the dentin. This can result in tooth sensitivity over time.
- Using abrasive dental care products: Certain toothpaste, mouthwashes, and teeth whitening products can contain abrasive ingredients that may contribute to enamel erosion and tooth sensitivity. It is important to choose dental care products that are specifically designed for individuals with sensitive teeth.
- Gum disease: Untreated gum disease can cause gum recession, exposing the sensitive tooth roots. This can lead to heightened tooth sensitivity.
- Age: As individuals age, the enamel layer on teeth naturally becomes thinner, making the dentin more susceptible to exposure and tooth sensitivity.
- Dental procedures: Certain dental treatments, such as teeth whitening, dental cleanings, or orthodontic adjustments, may cause temporary tooth sensitivity. This is usually temporary and resolves on its own.
It is essential to address these lifestyle factors to help alleviate tooth sensitivity and maintain oral health. Consulting with a dentist can provide personalized recommendations and treatment options based on individual needs.
Diagnosis and Evaluation of Sensitive Teeth
To properly diagnose and evaluate sensitive teeth, a dentist will typically conduct a comprehensive examination and gather information about the patient’s dental history. This includes asking about any recent trauma, oral habits, and the nature of the sensitivity experienced.
The dentist may also perform various tests to determine the underlying cause of tooth sensitivity. One common test is applying cold air or a cold stimulus to the affected tooth to assess its response. This helps identify if the sensitivity is caused by enamel erosion, decay, or exposed dentin.
Additionally, the dentist may use a dental explorer or probe to check for any signs of dental decay or gum disease. X-rays may also be taken to assess the condition of the tooth roots and underlying bone structure. These diagnostic tools help in ruling out other potential causes of tooth sensitivity and determining an appropriate treatment plan.
It is important to communicate openly with the dentist about any symptoms and concerns related to tooth sensitivity to ensure an accurate diagnosis. The dentist will use this information to develop an effective treatment approach tailored to the individual’s needs.
Preventive Measures for Tooth Sensitivity
Managing and preventing tooth sensitivity requires adopting certain preventive measures. By implementing these practices, individuals can minimize their discomfort and protect their teeth from further damage. Some preventive measures for tooth sensitivity include:
- Adopting proper oral hygiene habits: Regular brushing, flossing, and rinsing with fluoride mouthwash can help maintain good oral health and prevent tooth sensitivity. Using a soft bristled toothbrush and gentle brushing techniques is essential to avoid enamel erosion.
- Choosing a toothpaste for sensitive teeth: Using a toothpaste specifically formulated for sensitive teeth can help reduce tooth sensitivity. These toothpastes contain desensitizing agents that help block the sensation of pain and protect the exposed dentin.
- Avoiding acidic foods and drinks: Acidic foods and beverages, such as citrus fruits, carbonated drinks, and fruit juices, can weaken the tooth enamel and cause sensitivity. Limiting their consumption or rinsing the mouth with water after consuming them can help minimize the risk.
- Reducing teeth grinding: Teeth grinding, also known as bruxism, can contribute to tooth sensitivity. Wearing a nightguard can help protect the teeth and reduce sensitivity caused by grinding or clenching.
- Maintaining a balanced diet: A diet rich in calcium and vitamin D can promote healthy teeth and prevent sensitivity. Consuming dairy products, leafy greens, and fortified foods can help strengthen the teeth and reduce sensitivity.
- Avoiding excessive teeth whitening: While teeth whitening can enhance the appearance of teeth, excessive use of whitening products or procedures can lead to tooth sensitivity. It is important to follow the instructions provided by the dental professional and avoid over whitening.
- Regular dental check ups: Routine dental check ups are essential for maintaining oral health and identifying any potential issues early on. Regular cleanings and examinations can help prevent tooth sensitivity and address any dental problems promptly.
By incorporating these preventive measures into daily oral care routines and lifestyle choices, individuals can effectively manage tooth sensitivity and maintain optimal oral health.
Professional Treatment Options for Sensitive Teeth
When it comes to managing sensitive teeth, it is important to seek professional guidance for appropriate treatment options. Dentists can provide targeted treatments to address the underlying causes and alleviate tooth sensitivity. Here are some professional treatment options for sensitive teeth:
- Desensitizing agents: Dentists can apply desensitizing agents, such as fluoride varnishes or bonding agents, to the sensitive areas of the teeth. These agents work by blocking the nerve pathways and reducing sensitivity.
- Dental sealants: Dental sealants are thin, protective coatings applied to the chewing surfaces of the teeth. They help to seal off exposed dentin and provide a barrier against sensitivity triggers like hot or cold stimuli.
- Tooth colored fillings: If tooth sensitivity is caused by dental decay or cavities, tooth colored fillings can help to restore and protect the affected teeth. These fillings are made of composite resin and are matched to the color of your natural teeth.
- Dental restorations: In some cases, more extensive dental restorations, such as crowns or inlays, may be necessary to treat tooth sensitivity. These restorations not only improve the aesthetics of the teeth but also provide added protection against sensitivity.
- Fluoride treatments: Dentists may recommend professional fluoride treatments to strengthen enamel and reduce tooth sensitivity. Fluoride helps to remineralize the teeth, making them more resistant to sensitivity triggers.
- Root canal therapy: If tooth sensitivity is severe and persistent, root canal therapy may be necessary. This procedure involves removing the nerve tissue from the tooth and sealing it to eliminate sensitivity and infection.
- Orthodontic treatment: Sometimes, tooth sensitivity can be caused by improper teeth alignment. In such cases, orthodontic treatment, such as braces or aligners, can help correct the alignment, reducing sensitivity.
It is important to remember that the appropriate treatment option for sensitive teeth may vary depending on the individual case. Consulting with a dentist will help determine the most suitable treatment plan for your specific needs. Professional treatment can provide long lasting relief from tooth sensitivity and improve your overall oral health. Contact us.
Long Term Management of Sensitive Teeth
Managing sensitive teeth in the long term requires a proactive approach to oral hygiene and lifestyle choices. Here are some tips to help minimize tooth sensitivity and maintain oral health:
- Maintain a proper oral hygiene routine: Brush your teeth at least twice a day using a soft bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste. Be gentle and avoid brushing aggressively, as it can wear down enamel and exacerbate tooth sensitivity. Flossing daily is also important to remove plaque and prevent gum disease.
- Use desensitizing toothpaste: Consider using a desensitizing toothpaste that contains compounds like potassium nitrate or strontium chloride. These ingredients help to block the pain signals from reaching the nerve endings in your teeth, reducing sensitivity over time. Apply the toothpaste directly to the sensitive areas and use it regularly for lasting results.
- Avoid acidic and sugary foods: Acidic foods and drinks can erode tooth enamel, leading to increased tooth sensitivity. Limit your consumption of citrus fruits, sodas, and sports drinks. It’s also important to reduce your intake of sugary foods and beverages, as they can contribute to tooth decay and gum problems.
- Don’t forget the fluoride: Fluoride remineralizes and strengthens tooth enamel, making it more resistant to sensitivity. Use fluoridated mouth rinses or consider using a fluoride gel recommended by dentist. Additionally, drink fluoridated water or ask dentist about fluoride treatments during regular dental visits.
- Avoid teeth grinding: Grinding or clenching your teeth can wear down enamel, making teeth more sensitive. If you have a teeth grinding habit, consider wearing a mouthguard at night to protect your teeth. Talk to dentist if you suspect teeth grinding issues.
- Attend regular dental check ups: Regular dental visits are essential for long term management of tooth sensitivity. Dentist will assess your oral health, provide professional cleanings, and address any underlying dental issues contributing to sensitivity.
By following these long term management strategies, you can effectively reduce tooth sensitivity and maintain optimal oral health. Remember, it’s crucial to consult dentist if you experience persistent or severe sensitivity, as it could be a sign of an underlying dental problem that requires professional treatment.