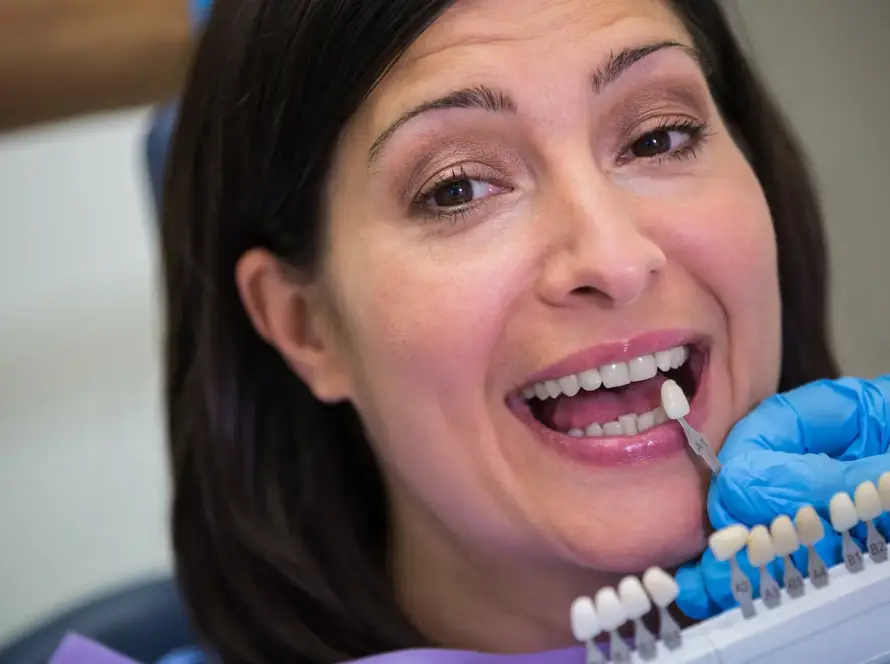
Receding gums, also known as gingival recession, occur when the margin of the gum tissue surrounding the teeth pulls back, exposing more of the tooth or its root. This condition can lead to tooth sensitivity, increased vulnerability to decay, and eventual tooth loss if left untreated. Understanding the underlying causes and signs is crucial for effective prevention and management.
Common Causes
– Poor Oral Hygiene: Inadequate brushing and flossing can lead to plaque buildup.
– Aggressive Brushing: Brushing too hard can wear away gum tissue.
– Gum Disease: Periodontal diseases like gingivitis and periodontitis.
– Tobacco Use: Smoking and chewing tobacco contribute to gum problems.
– Hormonal Changes: Women’s hormonal fluctuations can affect gum health.
Signs to Watch For
– Tooth sensitivity
– Longer-looking teeth
– Visible tooth roots
– Swollen or red gums
– Bleeding after brushing or flossing
Anatomy of Healthy Gums
Healthy gums typically exhibit the following characteristics:
1. Color: Healthy gums are usually a consistent shade of pink. Any redness or white patches might indicate a problem.
2. Texture: Firm and resilient to the touch. They should not be swollen or spongy.
3. Contour: Gums should fit snugly around each tooth, creating a scalloped edge.
4. Bleeding: Minimal to no bleeding when brushing or flossing, suggesting robust gum tissue.
5. Moisture: Gums are adequately moist, not dry or overly shiny.
6. Sensitivity: Minimal sensitivity to temperature changes or pressure.
7. Pocket Depth: Healthy gums feature shallow spaces (pockets) between the gums and teeth, typically 1-3 millimeters.
Proper oral hygiene and regular dental check-ups are essential to maintaining these characteristics.
Common Causes of Gum Recession
– Poor Oral Hygiene: Insufficient brushing and flossing can lead to plaque buildup, which may result in gum recession.
– Periodontal Disease: Bacterial gum infections that destroy gum tissue and supporting bone.
– Aggressive Brushing: Brushing teeth too hard or using a hard-bristled toothbrush can wear down gums.
– Tobacco Use: Smoking and chewing tobacco contribute to gum recession by damaging gum tissue.
– Grinding and Clenching Teeth: Known as bruxism, this can exert excessive force on the gums.
– Genetics: Some individuals are more susceptible to gum recession due to inherited traits.
– Hormonal Changes: Fluctuations during pregnancy, menstruation, or menopause can make gums more sensitive.
Symptoms of Receding Gums
Identifying receding gums early is crucial to prevent further health complications. Common symptoms include:
– Sensitivity: Increased sensitivity to hot, cold, or sweet foods and drinks.
– Longer Teeth Appearance: Teeth appear longer due to more root exposure.
– Visible Roots: Exposed tooth roots are often noticeable.
– Discomfort: Pain or discomfort along the gum line.
– Gums Bleeding: Gums bleed easily during brushing or flossing.
– Spaces: New spaces forming between teeth can be observed.
– Bad Breath: Persistent bad breath or a bad taste in the mouth.
– Gum Color Changes: Gums may turn red, inflamed, or swollen.
Diagnosis of Gum Recession
Professionals diagnose gum recession through clinical examination and dental history. They assess:
– Visual Inspection: Identifying exposed tooth roots and discrepancies in gum line.
– Probing Depths: Measuring gingival sulcus depth using a periodontal probe.
– Dental X-rays: Capturing bone structure and teeth alignment.
– Medical History: Reviewing conditions affecting oral health—diabetes, medications.
– Plaque and Tartar: Checking for buildup contributing to gum disease.
Detection of early signs and symptoms:
– Sensitivity: Increased tooth sensitivity to temperature changes or brushing.
– Inflammation: Redness, swelling, or bleeding of gums.
– Tooth Appearance: Teeth appearing longer due to gum line recession.
Risk Factors Associated with Receding Gums
Various factors can contribute to receding gums, increasing an individual’s risk. These include:
– Poor Oral Hygiene: Insufficient brushing and flossing can lead to plaque buildup, causing gum recession.
– Aggressive Brushing: Using a hard-bristled toothbrush or brushing too hard can wear away gum tissue.
– Genetics: Family history can make individuals more susceptible to gum recession.
– Tobacco Use: Smoking or chewing tobacco deteriorates gum health.
– Grinding Teeth: Bruxism can intensify gum recession.
– Hormonal Changes: Pregnant women may experience gum sensitivity and recession.
– Medical Conditions: Diabetes and immune diseases can impact gum health.
Preventative Measures for Receding Gums
To effectively prevent receding gums, one should adhere to rigorous oral hygiene practices. Regular brushing and flossing are essential.
– Use a Soft-Bristled Toothbrush: This minimizes the risk of gum abrasion.
– Proper Brushing Techniques: Employ gentle, circular motions.
– Floss Daily: Reduces plaque build-up in hard-to-reach areas.
– Antimicrobial Mouthwash: Helps in lowering oral bacteria levels.
– Regular Dental Checkups: Professional cleaning and early detection of issues.
Additionally, lifestyle changes play a role. Avoid tobacco use, consume a balanced diet, and manage stress to support overall gum health.
Home Remedies for Managing Receding Gums
– Oil Pulling: Swish coconut oil or sesame oil for 15-20 minutes daily to reduce bacteria.
– Saltwater Rinse: Gargle with a mixture of salt and warm water to alleviate inflammation and kill bacteria.
– Aloe Vera: Apply aloe vera gel directly to gums to promote healing and reduce inflammation.
– Green Tea: Drink green tea to reduce periodontal inflammation and strengthen gums.
– Turmeric Paste: Apply a paste made from turmeric powder and water to gums to reduce swelling.
– Hydrogen Peroxide: Rinse with a diluted hydrogen peroxide solution to disinfect the mouth and relieve symptoms.
Professional Treatments for Gum Recession
Dentists employ various treatments for receding gums. One common method is scaling and root planing, a deep cleaning procedure removing plaque and tartar from below the gumline.
– Gum Grafting: Tissue is taken from another mouth part and grafted to the receding area.
– Pinhole Surgical Technique: A minimally invasive technique that involves making small holes to reposition gum tissue.
– Regeneration: Special proteins or grafts are applied to encourage bone and tissue growth.
Lasers may be used to remove diseased tissue and promote healing. Dentists tailor treatments based on the recession severity and patient needs.
Surgical Options for Severe Cases
When natural methods are insufficient, surgical intervention may be necessary to treat severe cases of receding gums. Various procedures can address gum recession effectively:
– Gum graft surgery: Tissue from another part of the mouth is grafted onto the receding gums to cover exposed roots.
– Flap surgery: The gums are lifted for deep cleaning, then sutured back tightly.
– Pinhole surgical technique: Small holes are made to stretch the gum tissue over receded areas.
– Regeneration: Grafting of tissue-stimulating proteins and membranes to regenerate gum and bone tissue.
Consultation with a periodontist is crucial for determining the best course of action.
The Role of Diet and Nutrition in Gum Health
Proper nutrition is essential for maintaining healthy gums. A diet rich in vitamins and minerals, particularly Vitamin C and calcium, helps in gum tissue repair and strengthens teeth. Foods that promote gum health include:
– Leafy greens like spinach and kale
– Fruits such as oranges and strawberries
– Dairy products like milk and yogurt
– Nuts and seeds
It’s crucial to limit sugar and acidic foods to reduce plaque buildup and inflammation. Drinking plenty of water and reducing alcohol consumption can also help keep gums healthy. High-fiber foods can cleanse teeth and gums, removing harmful bacteria.
The Psychological Impact of Receding Gums
The impact of receding gums extends beyond just physical health. It can significantly affect individuals psychologically. This condition may:
– Lower self-esteem due to the altered appearance of the gums and teeth.
– Increase anxiety about dental health and hygiene.
– Lead to social withdrawal because of embarrassment.
– Trigger stress from the fear of tooth loss.
These emotional responses can exacerbate the condition, as stress is known to affect oral health. Understanding this psychological impact is crucial for comprehensive management and should be addressed alongside physical treatments.
Long-term Outlook and Prognosis
Regular practice of natural gum health measures can offer sustained protection.
– Diet: Consistently consuming foods high in vitamin C and antioxidants.
– Oral Hygiene: Brushing with natural toothpaste and regular flossing.
– Preventive Measures: Routine dental check-ups to catch early signs of gum issues.
Over time, these practices can stabilize gum recession and potentially reverse minor cases. Education on proper techniques and a disciplined approach remain crucial. Adherence is key to achieve long-term benefits while mitigating risks. Consistent attention to gum care can result in healthier gums and a lower likelihood of advanced periodontal disease.
Frequently Asked Questions about Receding Gums
What are the common causes of receding gums?
– Poor oral hygiene
– Aggressive brushing
– Periodontal disease
– Genetic predisposition
– Hormonal changes
– Use of tobacco products
Can receding gums grow back naturally?
Receding gums do not grow back naturally. However, maintaining proper oral hygiene and using natural remedies can help slow down the process and prevent further recession.
What natural remedies can help manage receding gums?
– Oil pulling with coconut or sesame oil
– Rinsing with saltwater
– Applying aloe vera gel
– Using a soft-bristled toothbrush
– Consuming green tea
When should one seek professional care?
– Severe gum recession
– Persistent pain or swelling
– Bleeding gums despite natural remedies
– Difficulty eating or speaking
Is receding gums a sign of gum disease?
Yes, receding gums can be an early sign of periodontal disease, highlighting the need for professional evaluation.
Conclusion and Final Thoughts
Natural methods can be effective in preventing and managing receding gums. Implementing proper oral hygiene practices, such as regular brushing and flossing, is essential. Dietary considerations, including reducing sugar intake and consuming foods rich in vitamins, play a crucial role in maintaining gum health.
Key Strategies:
– Oral Hygiene: Brush twice daily and floss regularly.
– Dietary Choices: Opt for vitamin-rich foods and limit sugary treats.
– Routine Checkups: Regular dental visits for professional cleanings and assessments.
– Natural Remedies: Consider gentle massages with essential oils or saline rinses.
Continuous attention to these practices contributes to healthier gums and overall oral wellness.