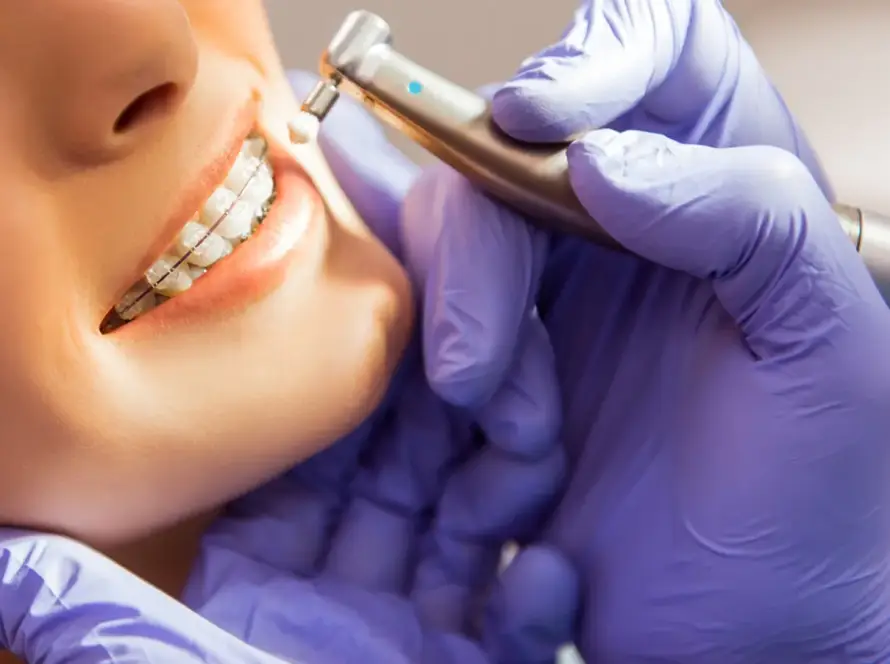
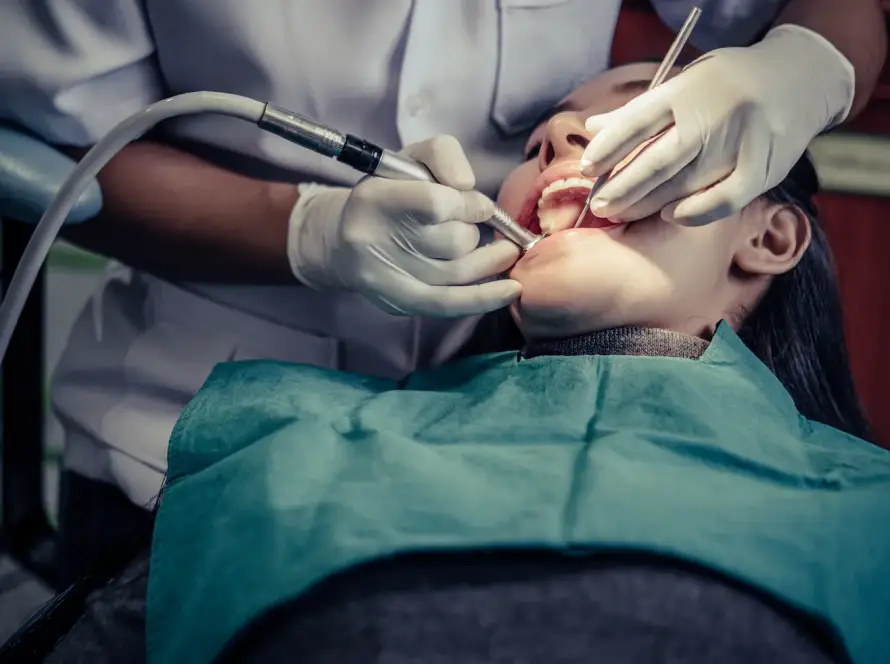
Calcium Deposits on Teeth
Calcium deposits on teeth, also known as dental calculus or tartar, are hardened mineral build ups on the teeth. These deposits are typically caused by the accumulation of plaque, a sticky film of bacteria and food particles, on the teeth and along the gumline.
When plaque is not properly removed through regular brushing and flossing, it can harden and turn into tartar. Calcium and other minerals in saliva contribute to the hardening process, causing the formation of calcified deposits on the teeth.
Calcium deposits on teeth can vary in color, ranging from yellowish to brownish. They usually appear as rough, hard areas on the teeth, which can be felt with the tongue or visually detected by a dental professional during an oral examination.
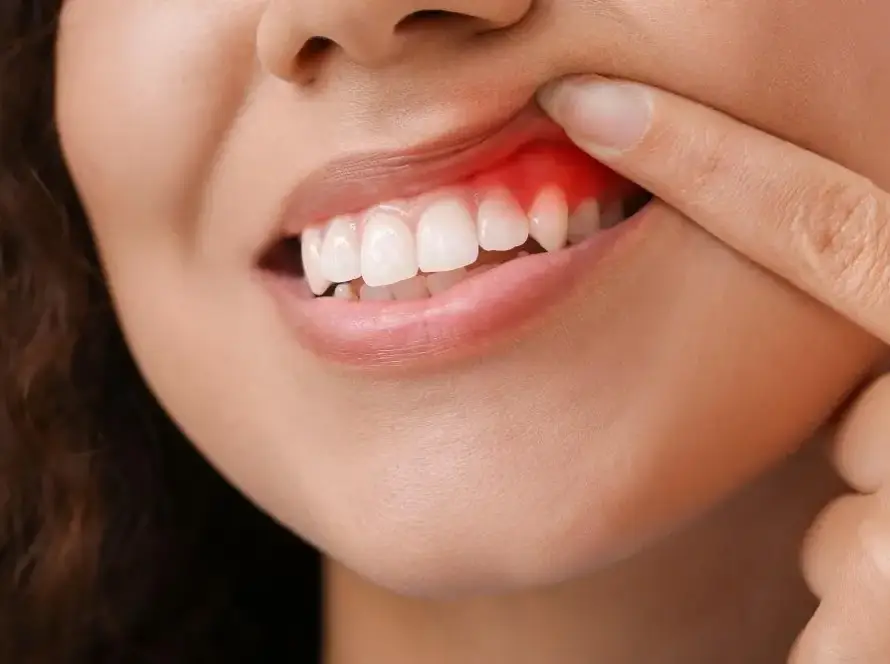
These deposits not only affect the appearance of the teeth but can also lead to various dental problems. Tartar buildup can irritate the gums, leading to inflammation and gum disease. It can also provide a favorable environment for bacteria to thrive, increasing the risk of tooth decay and bad breath.
Regular dental cleanings by a dental professional are necessary to remove tartar and prevent its further accumulation. During a dental cleaning, the deposits are carefully scraped off the teeth using specialized tools. In some cases, a procedure called scaling and root planing may be necessary to remove tartar from below the gumline.
Prevention is key in avoiding calcium deposits on teeth. Good oral hygiene practices, such as brushing twice a day, flossing daily, and using an antiseptic mouthwash, can help prevent plaque buildup. Additionally, maintaining a balanced diet and avoiding sugary and acidic foods can contribute to overall dental health.
In conclusion, understanding calcium deposits on teeth is crucial for maintaining good oral hygiene. Regular dental check ups and cleanings, along with proper oral care at home, can help prevent tartar buildup and ensure a healthy smile.
Causes of Calcium Deposits on Teeth
- Poor oral hygiene: Insufficient brushing and flossing can lead to the buildup of plaque, a sticky film containing bacteria. Over time, this plaque can harden and form calcium deposits on the teeth.
- Excessive calcium intake: Consuming an excess of calcium rich foods or supplements may contribute to the formation of calcium deposits on the teeth. This can occur if the body cannot effectively eliminate the excess calcium, leading to its deposition on the teeth.
- Salivary gland dysfunction: Saliva plays a crucial role in maintaining oral health by helping to wash away food particles and neutralize acids. If the salivary glands are not functioning properly, there may be a decrease in saliva production, which can result in the formation of calcium deposits.
- Tooth enamel erosion: Acidic foods and beverages, such as citrus fruits, soda, and energy drinks, can erode the protective tooth enamel. When the enamel is weakened, calcium salts can accumulate and form deposits on the teeth.
- Medical conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as Sjögren’s syndrome or dry mouth syndrome, can disrupt saliva production and increase the risk of calcium deposits on the teeth.
- Medications: Some medications, such as antihistamines or antidepressants, can cause dry mouth, which reduces saliva flow and promotes the formation of calcium deposits.
Remember, it is essential to maintain proper oral hygiene practices, visit your dentist regularly, and seek professional advice for the treatment and prevention of calcium deposits on teeth.
Effects of Calcium Deposits on Teeth
When calcium deposits form on the teeth, they can have several effects.
- Tooth Sensitivity: Calcium deposits can lead to increased tooth sensitivity. The build up of calcium can cause the enamel to become worn down, exposing the underlying dentin. This can result in increased sensitivity to hot or cold foods and beverages.
- Discoloration: Calcium deposits can cause teeth to appear yellow or discolored. This can be particularly noticeable when the deposits are located on the front teeth. The stains may be difficult to remove with regular brushing and can affect the overall appearance of the smile.
- Bad Breath: The presence of calcium deposits can contribute to bad breath. Bacteria can accumulate and thrive on the deposits, leading to an unpleasant odor.
- Gum Irritation: In some cases, calcium deposits can irritate the gums and lead to inflammation. This can cause the gums to become red, swollen, and tender, making brushing and flossing uncomfortable.
It is important to address calcium deposits on teeth to prevent further damage and maintain oral health.
Preventing Calcium Deposits on Teeth
Preventing calcium deposits on teeth is essential for maintaining optimal oral health. Here are some steps that can help prevent the formation of these deposits:
- Practice good oral hygiene: Brushing your teeth at least twice a day and flossing daily can help remove plaque and prevent the formation of calcium deposits. Use a fluoride toothpaste and a soft bristle toothbrush for effective cleaning.
- Limit sugary and acidic foods: Sugary and acidic foods can contribute to teeth decay and the buildup of plaque, which can lead to calcium deposits. Limiting the consumption of these foods can help prevent mineral accumulation on the teeth.
- Visit the dentist regularly: Regular dental check ups and professional cleanings play a crucial role in preventing calcium deposits. Your dentist can detect early signs of plaque and tartar buildup, and provide professional cleaning to remove them.
- Use fluoride mouthwash: Adding a fluoride mouthwash to your daily oral care routine can help strengthen your teeth and decrease the likelihood of calcium deposits forming.
- Drink plenty of water: Staying hydrated by drinking water throughout the day promotes saliva production. Saliva helps wash away bacteria and food particles, reducing the risk of plaque buildup and calcium deposits.
- Quit smoking: Smoking not only stains your teeth but also increases the risk of plaque formation. Quitting smoking can improve the overall health of your teeth and gums.
By following these preventive measures, you can reduce the risk of calcium deposits on your teeth and maintain a healthy smile. Remember, consult with your dentist for personalized advice and recommendations based on your specific oral health needs.
Professional Dental Treatments for Calcium Deposits
When it comes to dealing with calcium deposits on teeth, professional dental treatments can provide effective solutions. Here are some options:
- Professional Cleaning: Regular dental cleanings by a dental hygienist are essential for removing plaque and calculus buildup. A professional cleaning can help remove superficial calcium deposits and restore the natural whiteness of your teeth.
- Scaling and Root Planing: If the calcium deposits have progressed to a more advanced stage, scaling and root planing may be necessary. This deep cleaning procedure involves the removal of tartar both above and below the gumline. It helps to eliminate bacteria and promote gum health.
- Microabrasion and Polishing: For superficial calcium deposits, microabrasion may be recommended. This process involves the use of a gentle abrasive to remove the outer layer of enamel. Afterwards, polishing can be performed to restore the smoothness and shine of the teeth.
- Laser Treatment: In some cases, dentists may use laser therapy to remove calcium deposits. This non invasive technique targets the deposits and breaks them down without damaging the surrounding teeth or tissues.
- Veneers or Dental Bonding: In situations where the calcium deposits cannot be effectively removed, veneers or dental bonding may be considered. These cosmetic treatments involve the application of a thin layer of porcelain or composite resin to cover the affected teeth, providing a visually pleasing and natural looking solution.
It is essential to consult with your dentist to determine the most suitable treatment option for your specific needs. Remember, regular dental check ups and good oral hygiene habits are crucial in preventing calcium deposits and maintaining a healthy smile.
Home Remedies for Calcium Deposits
If you are dealing with calcium deposits on your teeth, there are some home remedies that you can try to help manage the condition. These remedies may not completely remove the deposits, but they can help minimize their appearance and prevent further buildup. Here are some home remedies that you can consider:
- Brushing and flossing: Maintaining good oral hygiene is crucial in preventing and managing calcium deposits. Brush your teeth at least twice a day and floss daily to remove plaque and reduce the chances of calcium buildup.
- Using baking soda: Baking soda has mild abrasiveness, which can help remove surface stains and calcium deposits. Mix a small amount of baking soda with water to form a paste and gently brush your teeth with it. Be careful not to use excessive force as it can damage the enamel.
- Oil pulling: This ancient remedy involves swishing oil around your mouth to remove toxins and promote oral health. Coconut oil is commonly used for this purpose. Take a tablespoon of coconut oil and swish it around your mouth for 10-15 minutes, then spit it out and rinse your mouth with water.
- Apple cider vinegar gargle: The acidic properties of apple cider vinegar can help dissolve calcium deposits. Mix one tablespoon of apple cider vinegar with a cup of water and gargle with it for a few minutes, then rinse your mouth with water.
- Vitamin C supplements: Vitamin C is known to promote healthy gums and can help reduce the formation of calcium deposits. Consult with your dentist or healthcare provider about the appropriate dosage of vitamin C supplements for you.
It’s important to note that while these home remedies may provide some relief, they are not a substitute for professional dental treatment. If you have severe or persistent calcium deposits, it’s essential to consult with your dentist for proper evaluation and treatment options.